Tools: Jupiter Notebook / Python / Pandas
Objectives
1. Identify the most popular programming languages among IT professionals.
2. Analyze average salaries and income statistics for IT professionals.
3. Explore the age distribution among IT professionals.
4. Provide statistical information on working hours for part-time and full-time IT professionals.
5. Examine the relationship between income and various factors such as working hours, age, education, and other variables.
6. Determine the most popular databases among IT professionals.
Tools:
Python, SQL, Postgres
Libraries:
numpy , pandas , seaborn , matplotlib.pyplot
Dataset:
Our data set is a survey works among IT professional , collected and published on Github in the link below.
It has 11551 records and 84 columns. (11552, 85)
Technical Objectives:
1. Connecting to API and import file
2. Save file into Data frame.
3. Cleaning the data (Nulls, outliers, rename, datatypes..)
4. Normalize the data frame and create data model where languages field moved into new data frame, so that include one piece of information per record each.
5. Transfer the new dataset into relational database or cloud.
6. Performing EDA
7. Visualizing & Plotting
Salaries: statistics for IT professionals.
The steps below were followed to clean the data and obtain a subset suitable for answering the compensation question:
- Removing duplicates, filter columns, remove nulls, and split the employment field.
- Creating a new column “earning” to standardize pay on an annual basis.
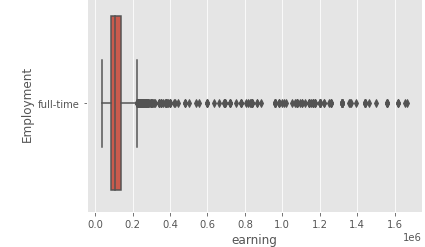
- Filtering the dataframe to including only USD compensations for full-time employees, excluding nulls and zeros, and remove outliers by completing the top and bottom 5% with median .
count 3,125.00
mean 152,928.26
std 207,792.90
min 38,272.00
25% 84,000.00
50% 106,000.00
75% 140,000.00
max 1,664,000.00
1. Central Tendency (The “Middle”)
- Mean (152,928.26): The arithmetic average of all values.
- 50% / Median (106,000.00): The exact middle value when the data is sorted.
- Interpretation: Because the mean is much higher than the median, your data is right-skewed (positively skewed). This typically occurs when a few very large values pull the average up, while most data points remain lower.
2. Spread and Variability
- Std (Standard Deviation: 207,792.90): This measures how far, on average, data points are from the mean. A standard deviation larger than the mean itself indicates extremely high variability and inconsistency.
- Min (38,272.00) & Max (1,664,000.00): These define the total range. The massive gap between the max and the 75th percentile (140k vs. 1.66M) confirms the presence of significant outliers at the high end.
3. Distribution Percentiles (Quartiles)
- 25% (84,000.00): One-quarter of your data is below this value.
- 75% (140,000.00): Three-quarters of your data is below this value, meaning the top 25% of your data starts at 140,000.
- Interquartile Range (IQR): The middle 50% of data falls between 84,000 and 140,000.
Summary Insight
Most of your data (75%) is relatively clustered between 38,272 and 140,000. However, the high-end outliers—reaching up to 1.66 million—are so extreme that they have nearly doubled the “average” (mean) relative to the “typical” (median) value. When reporting on this data, the median (106,000) is likely a more accurate representation of a “typical” entry than the mean.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.